X-rays were discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who received the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.
Radiology Accomplishments
Did you know? – Some interesting facts about Diagnostic Imaging
1895

1922

Marie Curie was the first woman to receive a Gold Medal from the Radiological Society of North America in 1922, and the American College of Radiology in 1931. With her discoveries of the radioactive elements radium and polonium, Marie Curie was the first person ever to receive two Nobel Prizes.
1930

X-rays became a part of popular culture in the 20th century because of their rumoured “mystical qualities.” Comic strip characters with “X-ray eyes” became popular and many people associated X-rays with fortune telling and the occult.
1932

The Nobel Prize Foundation recognizes many discoveries in physics, chemistry and medicine that have been made using X-rays.
1933

X-ray machines were a common sight in shoe stores from the 1930s to the early 1970s. Shoe-fitting “fluoroscopes” or “pedoscopes” were advertised as devices that made it easier to see how well a shoe fit. This was phased out as, knowledge about the long-term health consequences were identified and concerns about the unregulated use of radiation devices was better understood. This paved the way for the advancement of radiation safety.
1940

Ultrasound was developed for diagnostic purposes in the early 1940s. Doctor Karl Theodore Dussik of Austria published the first paper on medical ultrasonics in 1942 based on his research on transmission ultrasound investigation of the brain. During the 1950s, Professor Ian Donald of Scotland developed practical technology and applications for ultrasound and became known for producing the first useful images of fetuses.
1962

In 1962, Electric and Musical Industries, better known as EMI, signed a new group called ‘The Beatles’ to a recording contract that earned the company millions of dollars as a result. With extra money in the bank, EMI assigned Godfrey Hounsfield, a skilled physicist, to pursue independent research for EMI’s new electronic business. The result was his discovery of computed tomography and the creation of CT scanners.
1968

During the past 40 years, interventional radiologists have been responsible for much of the medical innovation and development of the minimally invasive procedures that are common today. Interventional radiologists pioneered modern medicine with the invention of angioplasty and the catheter-delivered stent, which were first used to treat peripheral arterial disease.
1970
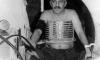
In 1970, Dr. Raymond Damadian, a medical doctor and research scientist discovered the basis for using magnetic resonance imaging as a tool for medical diagnosis. He found that different kinds of animal tissue emit response signals that vary in length, and that cancerous tissue emits response signals that last much longer than non-cancerous tissue. Less than two years later he filed his idea for using magnetic resonance imaging as a tool for medical diagnosis with the U.S. Patent Office, entitled “Apparatus and Method for Detecting Cancer in Tissue”. A patent was granted in 1974, it was the world’s first patent issued in the field of MRI. By 1977, Dr. Damadian completed construction of the first whole-body MRI scanner, which he dubbed the “Indomitable”.
1979

X-ray technology typically focuses on detecting small details inside the human body, but in 1979, the technology was turned towards larger targets when NASA used x-ray technology to take images of outer space. NASA helped pioneer the development of x-ray astronomy and continues to operate today. The Chandra X-ray Observatory, part of NASA’s fleet of “Great Observatories” allows scientists from around the world to obtain X-ray images of galactic environments to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe.
2003

In 2003, the Nobel Prize in Physiology of Medicine for 2003 was awarded jointly to Paul C. Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield for their discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
2004
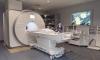
Worldwide, more than 60 million investigations with MRI are performed each year, and the method is still in rapid development with the emergence of clinical research in higher strength scanners capable of diagnosing many conditions with significantly more diagnostic detail.
2005

In 2005 the world’s first face transplant was performed. CT scans played an important role in the relatively new field of face transplantation, as CT imaging was critical to locate blood vessels and bony structures prior to the surgery and to assist the surgical team to estimate the amount of bone needed for upper and lower jaw transplants.
2009
The British Institute of Radiology’s Hugh Turvey ‘Artist in Residence’ in 2009, following his Oxo Gallery London exhibition titled: ‘X-perimentalist’ in which he showcased some 40 x-ray images to several thousand visitors, thereby introducing the public to the diagnostic image in a different light.
2010

In 2010, a set of three chest x-rays of Marilyn Monroe taken during a 1954 hospital visit sold for $45,000 in Las Vegas, at a movie memorabilia auction at Planet Hollywood.